
The alveolus is the smallest anatomical unit of the lung, and the site of gas exchange between the lung and the bloodstream. There are five or six alveolar sacs associated with each alveolar duct. Each terminal bronchiole then gives rise to several respiratory bronchioles, which go on to divide into two to 11 alveolar ducts. The segmental bronchi divide into many primary bronchioles that divide into terminal bronchioles. There are 10 segments in the right lung and 8 to 9 segments in the left lung due to anatomical differences. This property allows a bronchopulmonary segment to be surgically removed without affecting other segments. Each bronchopulmonary segment forms a discrete functional unit in the lung that is independent of the other segments. The lobar bronchi (also called secondary bronchi) divide into tertiary bronchi, each of which supplies air to a different bronchopulmonary segment.Ī bronchopulmonary segment is a distinct region of the lung separated from the rest of the lung by connective tissue. The right main bronchus subdivides into three lobar bronchi, while the left main bronchus divides into two. The right main bronchus is wider, shorter than the left main bronchus, which is thinner and longer.
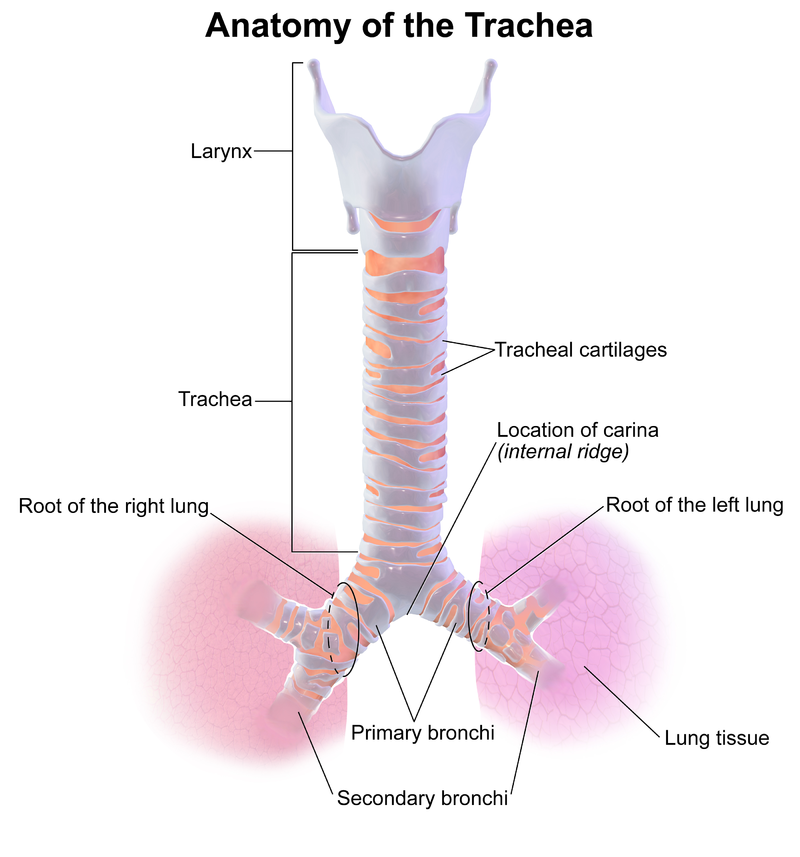
The point where the trachea divides into the bronchi is called the carina. The human trachea divides into two main bronchi (also called mainstem bronchi), that extend laterally (but not symmetrically) into the left and right lung respectively, at the level of the sternum.

The ratio of physiologic dead space to tidal volume is usually about 1/3. Alveolar dead space is the volume of gas within unperfused alveoli (and thus not participating in gas exchange either) it is usually negligible in the healthy, awake patient. Anatomic dead space is the volume of gas within the conducting zone (as opposed to the transitional and respiratory zones) and includes the trachea, bronchus, bronchioles, and terminal bronchioles it is approximately 2 mL/kg in the upright position. Physiologic or total dead space is the sum of anatomic dead space and alveolar dead space. Dead space is the volume of a breath that does not participate in gas exchange.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
